How Does It Work?
During an erection, blood flows through the penile arteries into two chambers known as the corpora cavernosa, which expand and harden the penis. These chambers are surrounded by a strong, elastic layer called the tunica albuginea. This structure also compresses the veins that would otherwise drain blood away, helping to maintain the erection.
In patients where other ED treatments have failed, penile prosthesis implantation offers a reliable and lasting solution. The procedure involves inserting an artificial penile device into the corpora cavernosa, replacing the function of the erectile tissue while maintaining a natural appearance and sensation. The prosthesis is encased by the tunica albuginea, allowing the penis to achieve the rigidity necessary for intercourse.
Local Anesthesia Technique
Traditionally, this surgery has been performed under spinal or general anesthesia. However, our clinic uses a modern dual-local anesthesia technique, including:
- Dorsal penile nerve block
- Peri-penile base tissue block
- Crural nerve block
This method involves injections only at the penile base (Figure 1). Patients remain awake and pain-free, and can use their phone or headphones during the procedure.

Figure 1: Dual-local anesthesia: dorsal nerve block, crural block (A), and base tissue block (B), administered at the penile base only.
Surgical Incisions
- A small circumcision-like incision under the glans
- A single 3 cm incision at the pubic area or penoscrotal junction
Hospital Stay
No hospitalization is required. Patients can walk and return home the same day.
Surgical Procedure Overview
Performed in the supine position under precise dual-local anesthesia, the procedure varies depending on the type of prosthesis used.
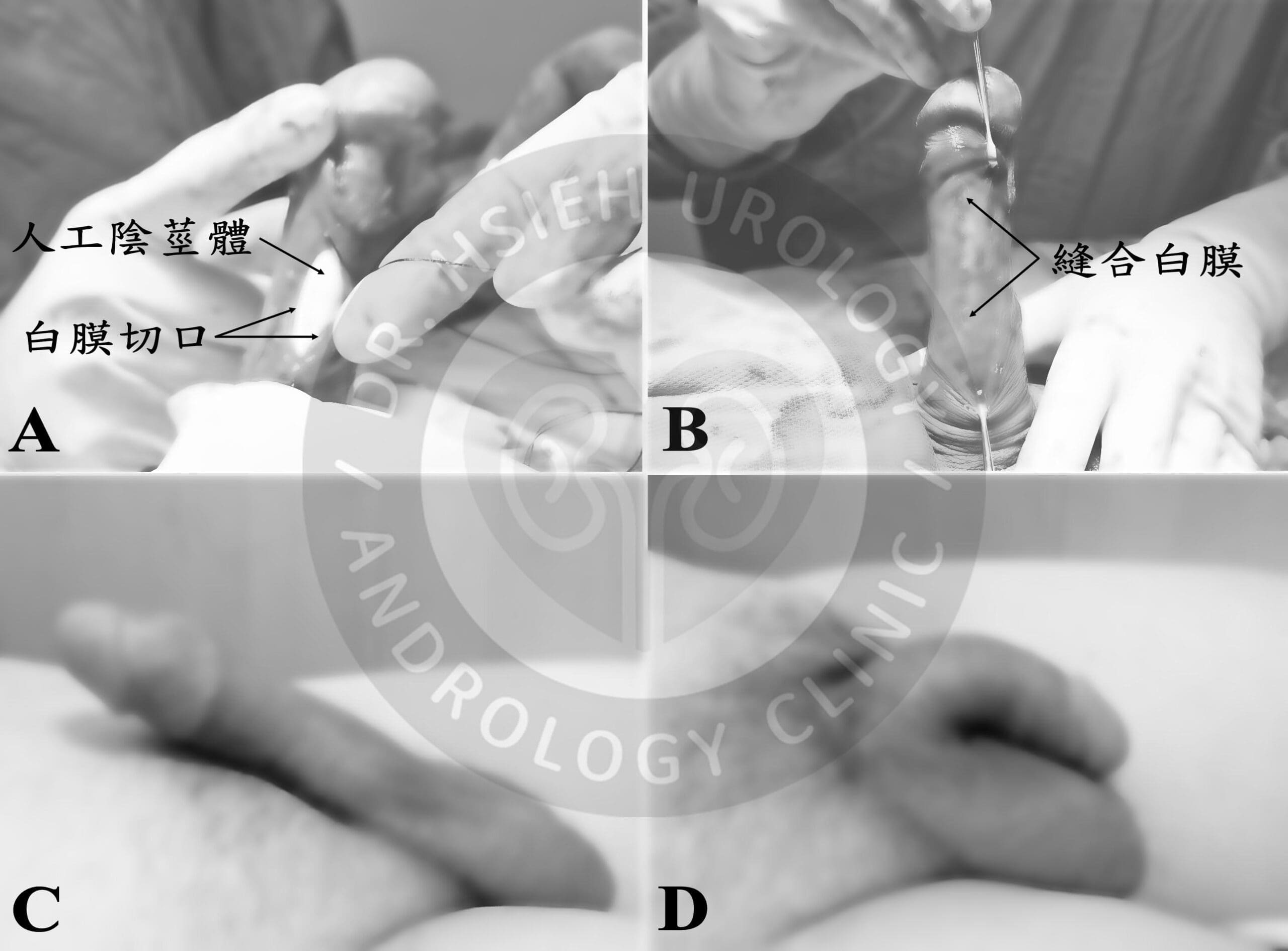
Using microsurgical techniques, tissues are carefully dissected to avoid damaging nerves and blood vessels. The tunica albuginea is exposed and incised on both sides of the penis, allowing the chosen prosthetic device to be inserted into the corpora cavernosa (Figure 2A). The tunica is then precisely sutured (Figure 2B).
For non-inflatable (semi-rigid) prostheses, the surgery ends here. The prosthesis can be manually bent upward for intercourse (Figure 2C) or downward afterward (Figure 2D), as shown in Figure 3.

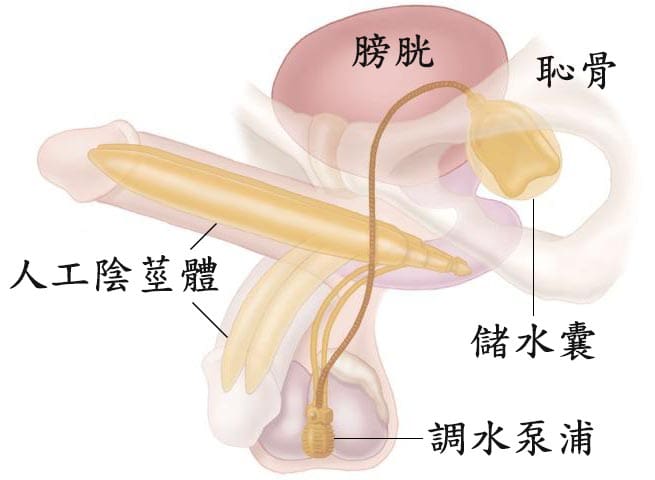
For three-piece inflatable prostheses, additional steps include placing:
- A pump inside the scrotum
- A reservoir behind the pubic bone, in front of the bladder
All components are connected by flexible tubing (Figure 5). Squeezing the pump inflates the prosthesis (Figure 4A); pressing the deflation button returns it to a flaccid state (Figure 4B).

Why Choose Our Clinic?
- Dual-local anesthesia
- Single small incision
- No hospitalization
- No electrocautery: minimal tissue damage and better healing
- Microsurgical precision based on detailed penile anatomy
Our approach is also used in other advanced surgeries:
- Microsurgical circumcision
- Hernia repair
- Varicocelectomy
- Penile curvature correction
- Testicular prosthesis implantation
- Vasectomy
- Penile dorsal nerve block surgery
Postoperative Outcomes
Penile prosthesis implantation is ideal for severe ED patients. Satisfaction rates range from 69% to 95%, with a domestic study showing 86.6% satisfaction. Type of prosthesis (inflatable vs. non-inflatable) did not significantly affect satisfaction.
Reported complication rates:
- Infection: 5.7%
- Mechanical failure: 6.6%
- Postoperative penile pain: 6.0%
- Prolonged foreskin edema: 5.4%
Studies show:
- 5-year mechanical survival rate for non-inflatable prostheses: 84%
- Inflatable prosthesis 1-year survival: 90%
- 5-year survival: 79.1%
- 10-year survival: 68.5%
- 15-year survival: 59.7%
Final Thoughts
While not a “natural” solution, penile prosthesis implantation remains one of the most effective treatments for ED. Whether using a semi-rigid or inflatable device, it restores functional erections while preserving orgasm and ejaculation.
This treatment should be considered as part of a comprehensive plan that includes:
- Counseling
- PDE5 inhibitors
- Shockwave therapy
- Hormone replacement therapy
When all other therapies fail, penile implant surgery offers renewed hope and restored intimacy.
註解: 資料來源
- 圖三:https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/products/penile-prosthesis/spectra-concealable-penile-prosthesis/features–benefits.html
- 圖五:https://www.bostonscientific.com/content/dam/bostonscientific/uro-wh/general/ams/hcp-resource-center-update/AMS-700-with-InhibiZone.jpg
期刊論文
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Chen SC, Chen YC, Liu LJ, Mok MS, Wu CH. Outpatient penile implantation with the patient under a novel method of crural block (以新的陰莖腳局部麻醉方法施行陰莖植入門診手術). International Journal of Andrology. 27:147-151, 2004.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chen HS, Ling PY, Wen HS, Liu LJ, Chen CW, Chua C. The advancement of pure local anesthesia for penile surgeries: can an outpatient basis be sustainable (純粹局部麻醉施行陰莖手術的新進展)? Journal of Andrology. 28(1):200-205, 2007.
- Hsu GL, Zaid UX, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Huang SJ. Acupuncture assisted local anesthesia for penile surgeries (針灸輔助局部麻醉下施行陰莖手術). Translational Andrology and Urology. 2(4):291-300, 2013.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Chen YC, Chen RM, Chen SC, Hsieh JT. The effect of electrocoagulation on the sinusoids in the human penis (電燒止血對於人類陰莖海綿體的影響). Journal of Andrology. 25(6):954-959, 2004.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Wu CH, Fong TH, Chen SC, Tseng GF. Anatomy of the human penis: the relationship of the architecture between skeletal and smooth muscles (人類陰莖解剖構造:骨骼肌和平滑肌之間的結構關係). Journal of Andrology. 25:426-431, 2004.
- Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu SP, Hsu GL, Chen HS, Molodysky E, Chen YH, Yu HJ. Advances in understanding of mammalian penile evolution, human penile anatomy and human erection physiology: Clinical implications for physicians and surgeons (了解哺乳類動物的陰莖進化、人類陰莖解剖學和人類勃起生理學方面的進展:對於內外科醫生的臨床意涵). Medical Science Monitor. 18(7): RA118-125, 2012.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chen SC. Human penile tunica albuginea: anatomy discovery, functional evidence and role in reconstructive and implant surgery (人類陰莖白膜:解剖學發現、功能上證據和在重建及人工陰莖植入手術中的角色). Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science. (GARJMMS) 3(12):400-407, 2014.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Chen YC, Chen SC, Mok MS. Penile venous anatomy: an additional description and its clinical implication (陰莖靜脈解剖構造:附加描述及其臨床意涵). Journal of Andrology. 24(6):921-927, 2003.
- Hsu GL, Wen HS, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu LJ, Chen YC. Traumatic glans deformity: reconstruction of distal ligamentous structure (外傷性龜頭畸形:重建遠端韌帶結構). Journal of Urology. 166:1390, 2001.
- Hsu GL, Lin CW, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Hsieh JT, Chen SC, Kuo TF, Ling PY, Huang HM, Wang CJ, Tseng GF. Distal ligament in human glans: a comparative study of penile architecture (人類龜頭遠端韌帶:一項比較研究陰莖結構). Journal of Andrology. 26(5):624-28, 2005.
- Hsu GL, Hill JW, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu SP, Hsu C. Venous ligation: a novel strategy for glans enhancement in penile prosthesis implantation (靜脈綁紮手術: 人工陰莖植入手術時增大龜頭的新方法), in Genitourethral Reconstruction, Ralf Herwig R, Sansalone S, Rehder P, Editors. BioMed Research International. Published special issue, Article ID923171, 7 pages, 2014.
- Hsieh CH (謝政興), Hsu GL, Chang SJ, Yang SSD, Liu SP, Hsieh JT. Surgical niche for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (手術治療勃起功能障礙的利基). International Journal of Urology. 27(2):117-133, 2020.
書籍著作
- Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興)、Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕). 治療勃起功能障礙 – 手術治療(Erectile Dysfunction – Surgical Management).書名:男性性功能障礙 – 臨床診治全攻略 (Male Sexual Dysfunction – A Complete Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment), 陳煜、簡邦平、蔡維恭、陳卷書編輯. 合記圖書出版社, 2023. 第三篇,第17章,頁245-262.
- Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興)、Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕). 勃起功能障礙 – 手術治療 (Erectile Dysfunction – Surgical Treatment). 書名:臨床泌尿學 (CLINICAL UROLOGY). 郭漢崇、賴明坤、楊啟瑞、黃一勝、余燦榮、陳進典、崔克宏,編輯. 台灣泌尿科醫學會, 2012.第八篇,第54章,頁1037-1049.
- Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕)、Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興). 書名:A LABORATORY MANUAL FOR POTENCY MICROSURGERY (性功能顯微手術實驗訓練手冊). 許耕榕、謝政興,編輯.
參考文獻
- Goodwin WE, Scott WW. Phalloplasty. J Urol. 1952; 68: 903.
- Beheri GE. Surgical treatment of impotence. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966; 38: 92.
- Pearman RO. Insertion of a silastic penile prosthesis for the treatment of organic sexual impotence. J Urol. 1972; 107: 802-806.
- Small MP, Carrion HM, Gordon JA. Small-Carrion penile prosthesis: new implant for management of impotence. Urology 1975; 5: 479.
- Finney RP. New hinged silicone penile implant. J Urol 1977; 118: 585-587.
- Jonas U, Jacobi GH. Silicone-silver penile prosthesis: description, operative approach and results. J Urol. 1980; 123: 865-867.
- Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Management of erectile impotence: use of implantable inflatable prosthesis. Urology. 1973; 2: 80-82.
- Furlow WL. Inflatable penile prosthesis: Mayo clinic experience with 175 patients. Urology. 1979; 13: 166-171.
- Montague DK. Experience with semirigid rod and inflatable penile prostheses. J Urol. 1983; 129: 967-968.
- Burnett AL, Nehra A, Breau RH, et al. Erectile Dysfunction: AUA guideline. 2018;https://www.auanet.org/guidelines/non-oncology-guidelines/sexual-and-reproductive-health.
- Hellstrom WJG, Montague DK, Moncada I, et al. Implants, mechanical devices, and vascular surgery for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:501-523.
- Wilson SK, Carson CC, Cleves MA, et al. Quantifying risk of penile prosthesis infection with elevated glycosylated hemoglobin. J Urol. 1998; 159:1537–1539. discussion 9–40.
- Chiang HS, Wu CC, Wen TC. 10 years experience with penile prosthesis implantation in Taiwanese patients. J Urol. 2000; 163: 476-480.
- Wilson SK, Delk JR, Salem EA, Cleves MA. Long-term survival of inflatable penile prostheses: single surgical group experience with 2384 first-time implants spanning two decades. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:1074-1079.
- Brant MD, Ludlow JK, Mulcahy JJ. The prosthesis salvage operation: immediate replacement of the infected penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1996; 155: 155-157.
- Mulcahy JJ. Treatment alternatives for the infected penile implant. Int J Impot Res. 2003; 15(Suppl 5): S147-149.

